As a 3D robot guidance provider in the automation industry, we are frequently asked, “Is your product AI (artificial intelligence)?” to which the answer is typically “yes, but not in the way that you may know.” The current media coverage of large language models like OpenAI and ChatGPT makes the public aware of AI, which adds complexity to the question.
The majority of the public has a basic understanding of a branch of AI that is specifically referred to by ibm.com as “machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks”, because of coverage by major media sources. AI awareness has the public searching for its uses in the current software products they utilize for work and leisure. Understanding the distinction between different types of AI is crucial, especially in the realm of manufacturing automation. While media coverage focuses on machine learning and its capabilities, it’s imperative to discern its unpredictability in contrast to deterministic classic computer algorithms.
What are the Different Types of Artificial Intelligence?
Machine learning algorithms are trained using large data sets, while classic computer algorithms are written by software developers and execute in a more deterministic way. Machine learning algorithms are valuable for solving complex problems, but can generate or classify data in an unexpected or incorrect way, which can lead to mistakes. This software generates a model based on a training set and uses that model to decide what action to take in response to input data. Data sets can create unpredictable behaviors based on biased, imperfect, or incomplete training data sets. The unpredictability of machine learning means the algorithms need to be tested extensively before use in high-risk situations. Most manufacturing processes are high-risk situations where unpredictable machine learning is not suitable. While machine learning software is new, exciting, and can react in ways that seem more human than machine, it’s important to consider whether the manufacturing process should behave like a human, or a machine.
Where Does 3D Robot Guidance Fall Under the AI Umbrella?
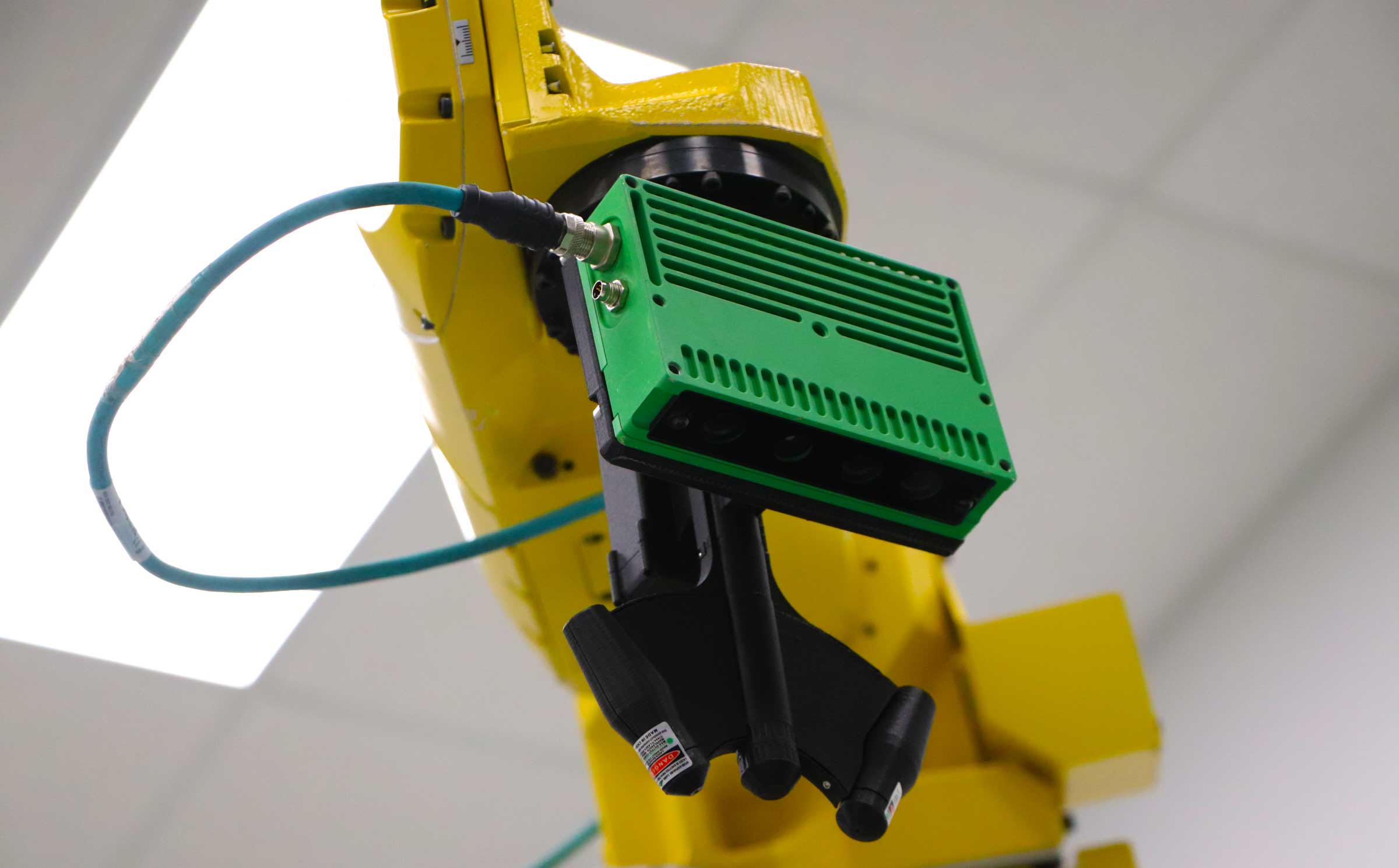
Machine Learning AI leverages computers and machines to mimic the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of the human mind (ibm.com). V-Guide™ is artificial intelligence, by definition, because V-Guide™ is computer vision for industrial robots. V-Guide™ 3D machine vision gives industrial robots the ability to interpret the environment and adjust their work to match the position of the part that is in the work zone. The system adds artificial intelligence to the robot work cell, but to be clear, V-Guide™ does not use machine learning algorithms and only takes preprogrammed actions for preprogrammed circumstances. When the system encounters a situation that it is not programmed for, it produces a fault and shuts the line down to maintain safety.
Navigating the Complexities of AI Implementation
In the realm of AI for manufacturing, understanding the distinction between machine learning algorithms and classic computer algorithms is vital. While both serve useful purposes, machine learning algorithms are prone to unpredictability. This poses risks, particularly in hazardous environments like manufacturing plants. The emphasis in manufacturing isn’t on AI replicating human behavior but rather on reliability and adherence to predetermined actions.
V-Guide™ uses artificial intelligence in manufacturing by leveraging computer vision to enhance industrial robots. Notably, V-Guide™ operates without machine learning algorithms, relying instead on preprogrammed actions, offering predictability and control that is vital for automated tasks.
Contact us for more information on our product offerings. Stay up to date with products and information by following us on LinkedIn.
